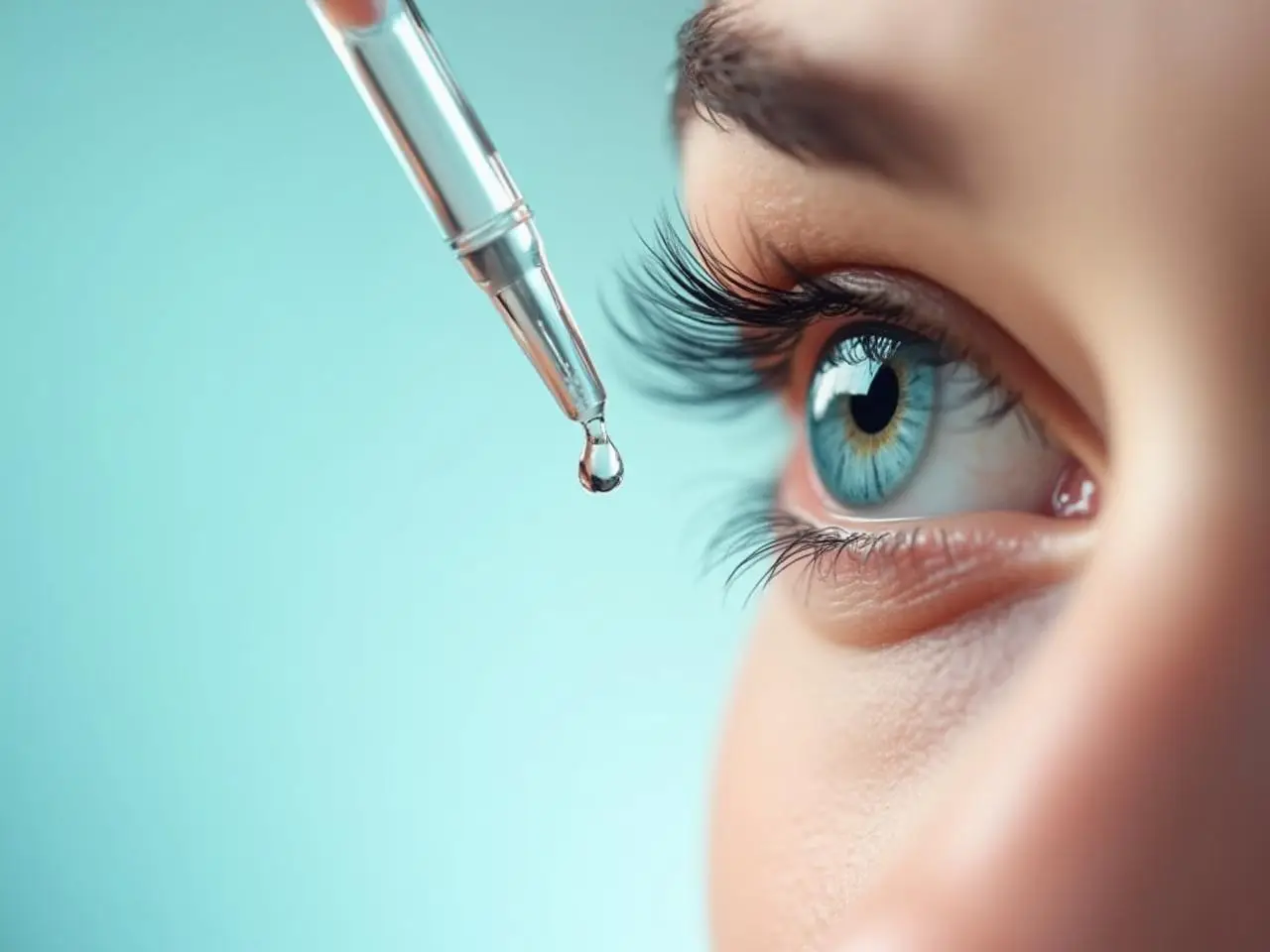
טיפות דמעות – מה זה ולמה משתמשים בהן?
טיפות דמעות הן תמיסות רפואיות או קוסמטיות שמטרתן להקל על
Eye infections can be broadly classified into several types based on the part of the eye they affect. Common types include conjunctivitis (pink eye), keratitis (infection of the cornea) and endophthalmitis (inner eye inflammation). Each type has its own causes and symptoms, which require different treatment approaches and treatment with antibiotic eye drops.
Eye infections are usually caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi or parasites. Factors that can increase the risk of developing eye inflammation include wearing contact lenses, exposure to contaminated water or air, eye injuries, a weak immune system, and a history of other eye diseases.
The symptoms of eye infections can vary but usually include redness, itching, swelling, discharge, pain, blurred vision, and increased sensitivity to light. Early detection of these symptoms is essential for rapid treatment to prevent complications.
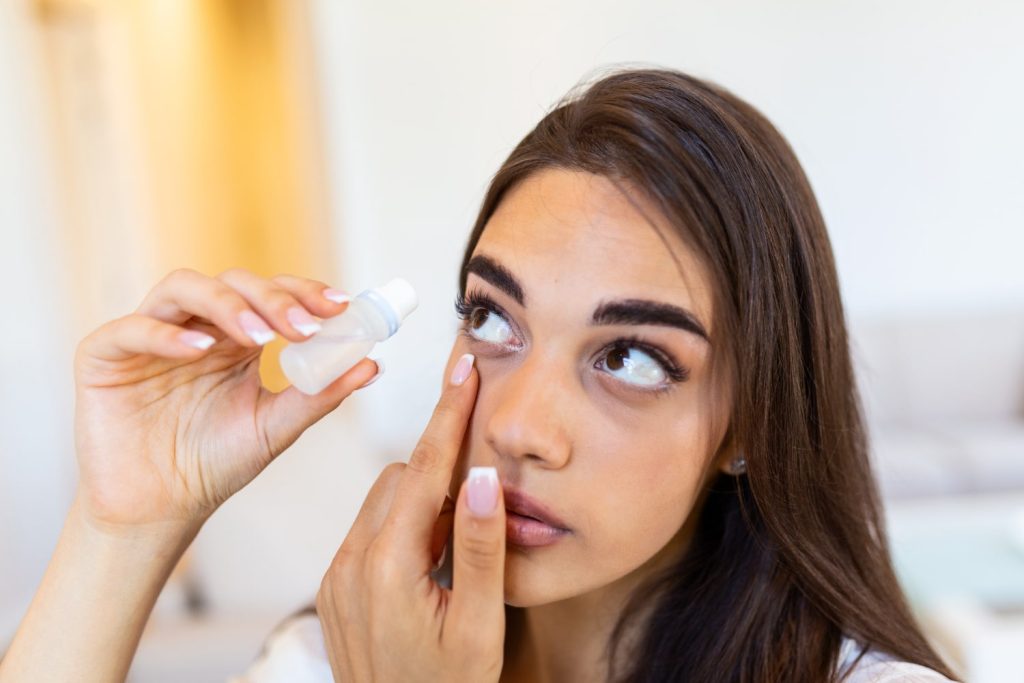

Antibiotics are drugs designed to fight bacterial infections. It works by killing bacteria or inhibiting their growth. In the case of eye infections, eye drops or antibiotic ointments are used to deliver the medicine directly to the infected area, which ensures a high concentration of the medicine at the site of the infection.
There are different types of antibiotic eye drops, each tailored to target specific types of bacteria. Common antibiotics include fluoroquinolones, aminoglycosides, macrolides, and sulfonamides. The choice of antibiotics depends on the type of bacteria causing the infection and the patient's medical history.
Antibiotics are also classified based on their spectrum of activity. Broad-spectrum antibiotics are effective against a wide variety of bacteria, making them the first choice for treating infections where the exact type of bacteria is unknown. Narrow-spectrum antibiotics, on the other hand, are effective against specific types of bacteria and are used when the causative agent is known.
Each type of antibiotic has specific indications. For example, fluoroquinolones are often reserved for more serious infections due to their broad-spectrum activity, while macrolides are preferred for patients with allergies to other antibiotics.
The effectiveness of antibiotics may vary depending on the type of bacteria. Fluoroquinolones, for example, are generally more effective against a wider range of bacteria than sulfonamides. However, the choice of antibiotic should always be guided by the specific infection and individual patient characteristics.
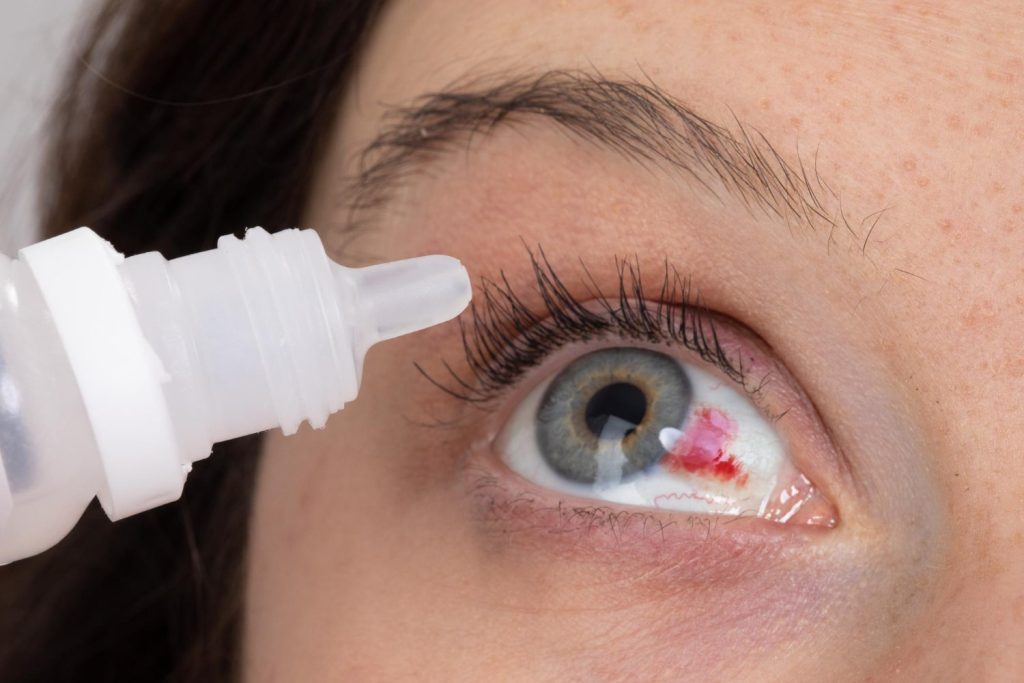
The dose and frequency prescribed for the course of treatment must be followed. Excessive use or excessively reduced use may lead to reduced effectiveness or an increased risk of side effects and resistance.
Complete the full course of treatment as prescribed, even if symptoms improve. Stopping treatment early may lead to relapse or resistance.
While antibiotic eye drops are generally safe, they can sometimes cause side effects such as mild stinging or burning when used, redness, itching, or an allergic reaction. Serious side effects are rare but can include blurred vision, swelling or worsening of symptoms, requiring immediate medical attention.
Some people may develop allergic reactions to certain antibiotics, manifested by redness, swelling or itching. It is important to inform the attending physician about known allergies before starting the treatment.
Antibiotic eye drops can interact with other medications, and may change their effectiveness. Always inform the attending physician of any medications or other supplements that are routinely taken.
Some antibiotic eye drops may not be suitable for children or pregnant women. It is essential to consult with a professional to understand the safest options in these populations.
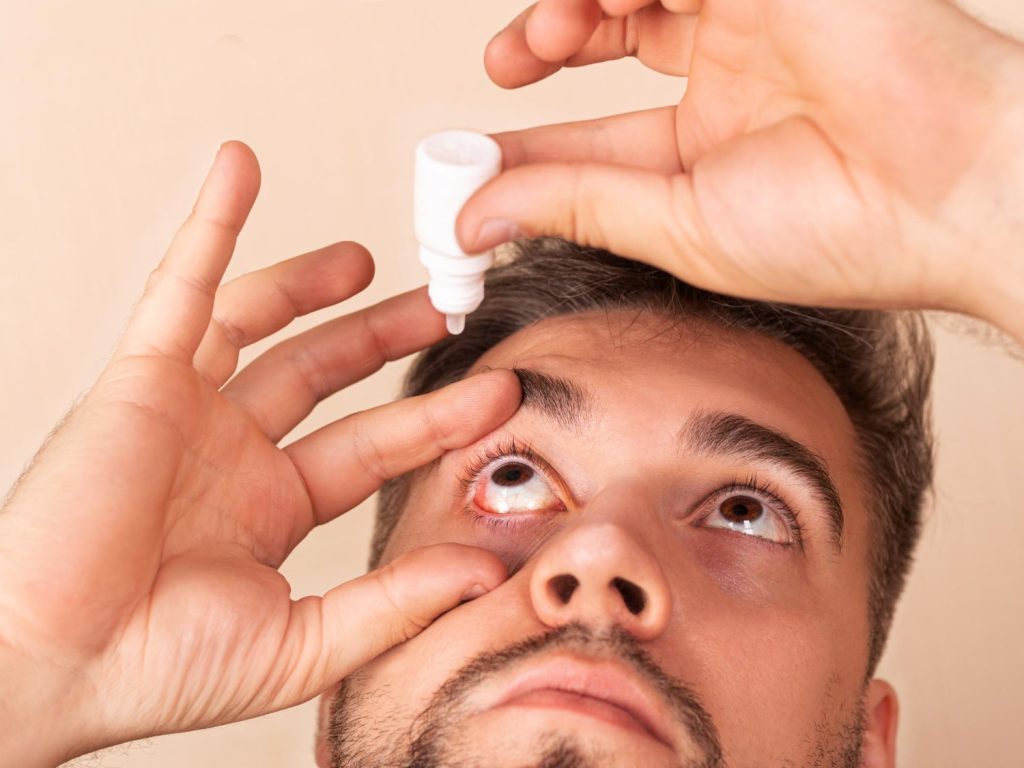
Antibiotic resistance occurs when bacteria evolve and become immune to its effects. This phenomenon is of increasing concern in the treatment of eye infections, as it may lead to reduced effectiveness of standard treatments, making it more difficult to treat infections. Infections that are resistant to antibiotics require alternative treatments, which may be less effective, more expensive or have more side effects. Therefore, prevention and proper use of antibiotics are extremely essential.
It is very important to understand the different types of eye infections and the role of antibiotic eye drops in their treatment. Emphasis must be placed on the proper use of these drugs, their safety considerations, and the imminent threat of antibiotic resistance. These drugs are intended to alleviate the symptoms of various eye diseases, but they must be used properly and wisely.

טיפות דמעות הן תמיסות רפואיות או קוסמטיות שמטרתן להקל על
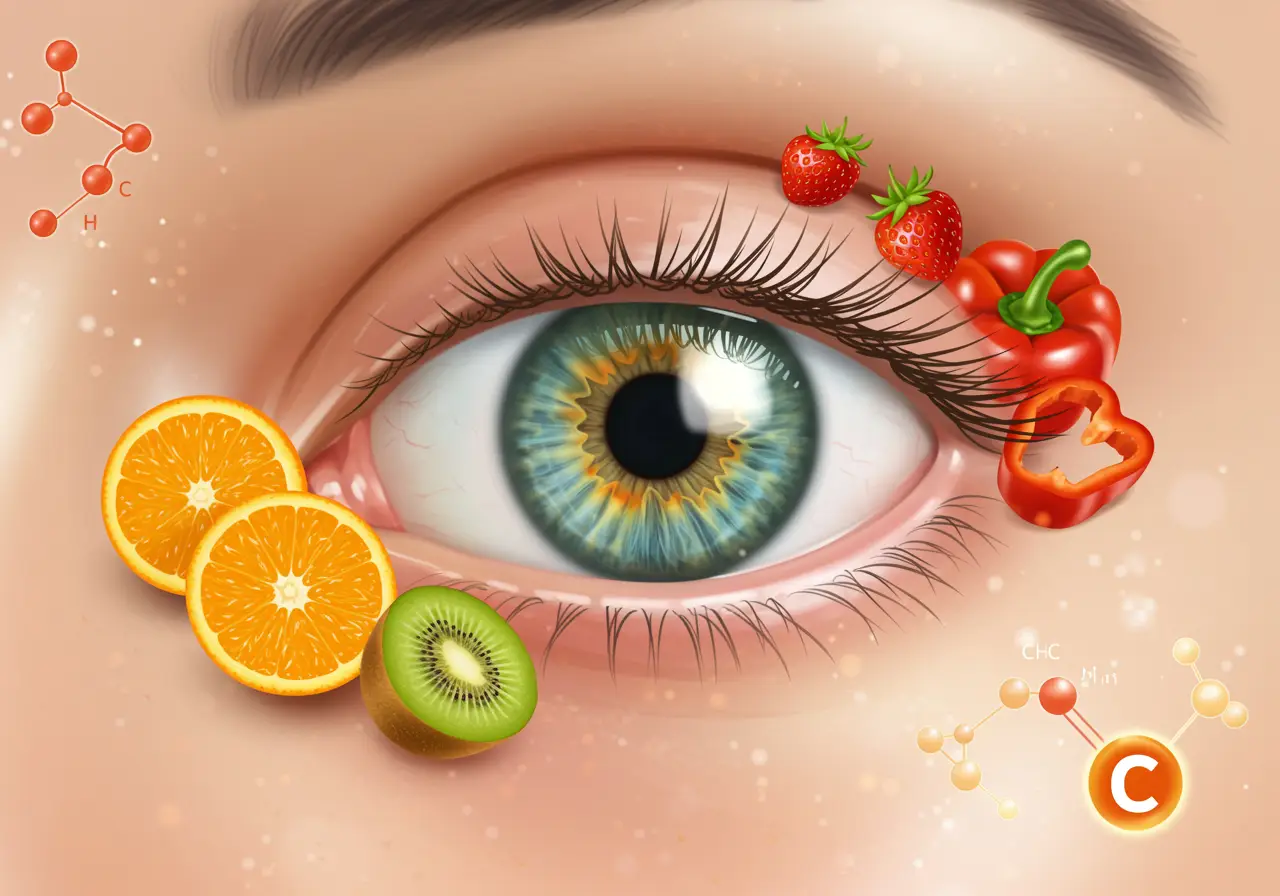

ויטמין C הוא אחד הוויטמינים החיוניים ביותר לבריאות העיניים, הודות
מרכז מומחים לאבחון וטיפול מתקדם בתסמונת העין היבשה ומחלות פני שטח העין