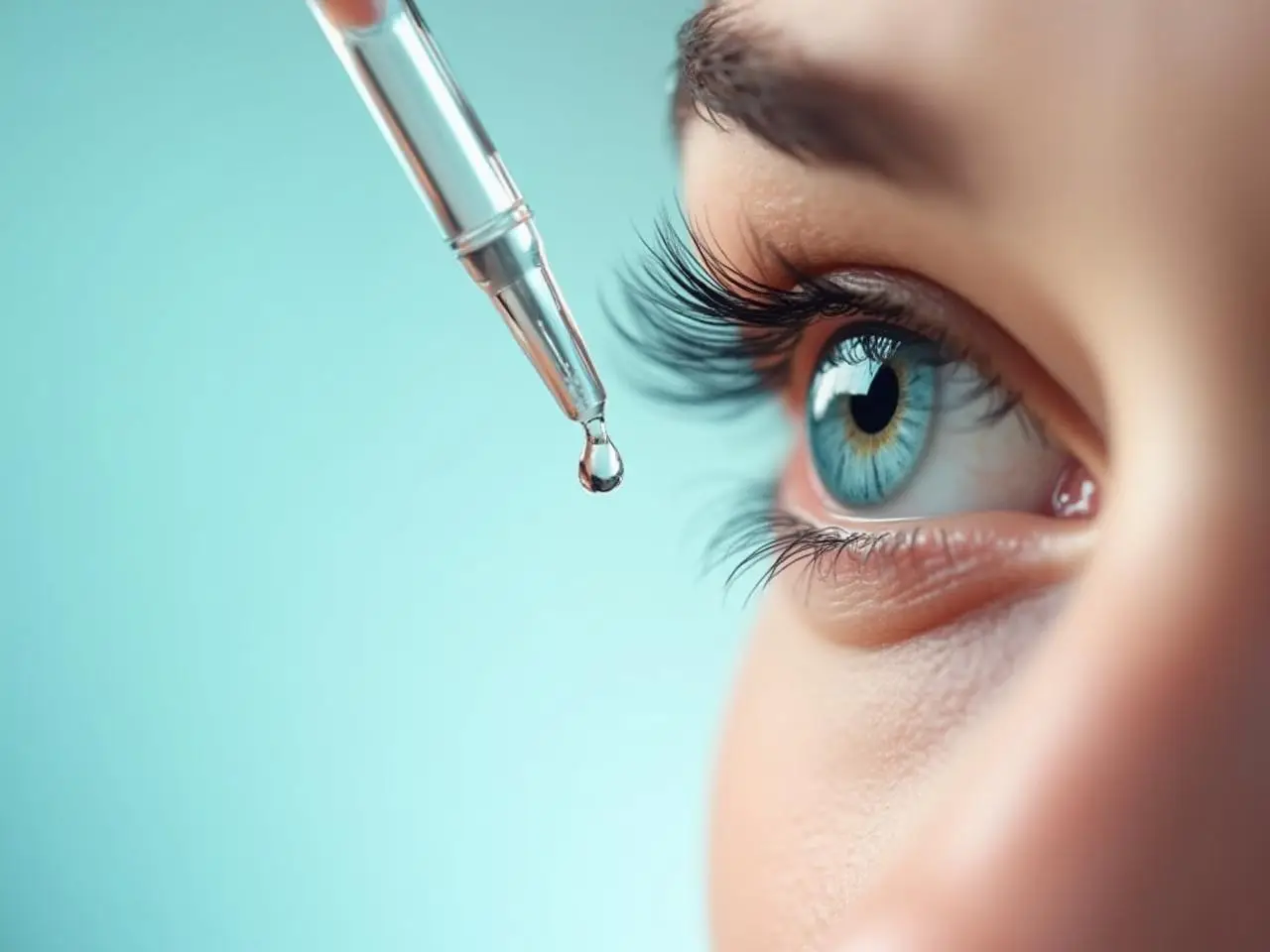
טיפות דמעות – מה זה ולמה משתמשים בהן?
טיפות דמעות הן תמיסות רפואיות או קוסמטיות שמטרתן להקל על
Tobrex, with its active ingredient tobramycin, has become a mainstay in the world of ophthalmology. As an antibiotic eye drop, it provides an essential line of defense against bacterial infections that can damage vision and eye health. With the sensitive nature of our eyes, timely care and proper use of effective treatments such as Tobrax play a critical role in maintaining new vision and healthy eyes.
The eyes are not only our windows to the world but also vulnerable portals to potential pathogens. Bacterial eye infections, if left untreated, can cause discomfort, decreased vision, and in severe cases, blindness. Ensuring prompt and adequate treatment of infections is extremely important. Moreover, with the world's growing concerns about antibiotic resistance, it is also essential to have reliable drugs that are both effective and safe. This is where Tobrax comes into the picture.
Tobrax, the active ingredient tobramycin, which was discovered in the 1970s, belongs to the group of aminoglycoside antibiotics. A product of the bacterium Streptomyces tenebrarius, it quickly gained recognition for its powerful antibacterial properties, making it a vital player in the fight against susceptible bacterial strains. Over time, its applications expanded, and it became a valued solution in ophthalmology, formulated as an eye drop or Tobrex ointment.
Tobramycin works by inhibiting protein synthesis in susceptible bacteria, leading to their eventual death. Specifically, it binds to the 30S ribosomal subunit of the bacterial ribosome. This binding interferes with the initiation complex between messenger RNA and the ribosome, thereby stopping protein synthesis. As a result, bacteria are unable to grow and reproduce, which reduces the spread of infection. Due to its mechanism of action, tobramycin is particularly effective against a variety of gram-negative bacteria, although it also has some activity against certain gram-positive bacteria.

Conjunctivitis : Often referred to as "pink eye," conjunctivitis is an inflammation of the conjunctiva, the thin, clear tissue that sits above the white part of the eye and inside the eyelid. Bacterial conjunctivitis can cause redness, itching and discharge, and Tobrax is usually prescribed to treat this condition.
Keratitis : This is an inflammation of the cornea, the clear front surface of the eye. Bacterial keratitis can be serious and sight-threatening if not treated immediately. Tobrax provides protection against various bacteria responsible for this condition.
Blepharitis : Although often related to other factors such as dandruff and dry eyes, a bacterial infection can worsen blepharitis, an inflammation of the eyelids. Using Tuberex ointment can help manage bacterial complications of this condition.
Eye surgeries may accidentally introduce bacteria into the eye, leading to infections after surgery. Tobrax is sometimes used prophylactically to reduce the risk of bacterial infections after certain eye procedures.
The standard dose of Tobrax varies according to the severity of the infection. Generally, for adults and children:
– For mild to moderate infections: drip 1-2 drops into the eye every 4 hours.
– For severe infections: drip a drop every hour until improvement, and then reduced frequency when the infection subsides.
The duration of treatment depends on the nature and severity of the infection. Most bacterial eye infections treated with Tobrax show improvement within 48 hours. However, it is essential to continue the medication for the prescribed duration, even if the symptoms have improved, to ensure complete elimination of the bacteria.
While Tobrax is generally well tolerated, as with any medicine, some people may experience side effects. The most common include:
Although rare, some people may experience more severe reactions. These include:
If you notice one of the serious side effects above:
Certain scenarios require a more cautious approach when considering Tobrax:
While Tobrax is primarily used topically, it is important to let your professional know if you are taking or have recently taken other medications, especially other topical eye medications.
Although there are limited data on the use of Tobrax during pregnancy, it should only be used if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus. Always consult a healthcare professional before using Tobrax if you are pregnant or breastfeeding.
Bacterial resistance to antibiotics is a growing concern worldwide. Resistance occurs when bacteria evolve and develop mechanisms to neutralize the effect of the antibiotic, rendering the drug ineffective. Several factors contribute to resistance:
The consequences of such resistance are significant. Infections become more difficult to treat, leading to prolonged illness, longer hospitalizations, and an increased risk of complications or even death.
In order for drugs like Tobrax to remain effective:

Efficacy : While Torbrax is very effective against a variety of bacteria, especially Gram-negative bacteria, its effectiveness may vary compared to other ophthalmic antibiotics depending on the pathogen. Some antibiotics may be stronger against certain strains of bacteria. The choice depends on the specific bacteria causing the infection.
Side effects : Every antibiotic has a profile of possible side effects. Some patients may tolerate Tobrax better than other antibiotics, while others may experience fewer side effects with alternatives to Tobrax.
Cost : The price of Tubrax is generally considered reasonable, but costs may vary depending on location, insurance coverage, and specific formulations. Comparatively, some of the alternative antibiotics may be more or less expensive.
There are scenarios where Tobrax may be a preferred choice:
Tobrax, like many eye solutions, requires specific storage conditions to maintain its effectiveness:
Always check the expiration date on the package before using Tobrax. Expired medicine may not be effective and may even be harmful. Once opened, a bottle of Tobrax should usually be used within a month. Always refer to the manufacturer's instructions for specific instructions.
Before administering, always wash your hands thoroughly. Do not touch the tip of the dropper with your hands or any surface, as this may introduce contaminants. Make sure the bottle cap is tightly closed after each use to prevent contamination and evaporation.
Many patients have found relief from bacterial eye infections using Tobrax. Commonly reported benefits include:
However, as with all medications, some people report drawbacks, including:
Sara from Rehovot : "Tobrax was a lifesaver when I developed a nasty eye infection. Within days, the redness and discharge disappeared. Although I felt a slight sting when I first applied it, it passed quickly."
Michael from Kfar Saba : "I had recurring eye infections, and Tobrax was always my choice. It works quickly and effectively. However, I always worry about using antibiotics too often."
Tobrax, with its active ingredient tobramycin, is a testament to advances in eye care and our ongoing fight against bacterial infections that threaten our vision. Its effectiveness, ease of use, and generally mild side effect profile have made it a preferred choice for many healthcare professionals and patients alike.
However, as with all antibiotics, the potential for bacterial resistance remains a concern. This emphasizes the importance of judicious use, patient education, and adherence to a prescribed treatment protocol. In the ever-evolving landscape of medicine, Tobrax is a reminder that while we have powerful tools at our disposal, responsible use is paramount.
For anyone considering using Tobrax, consultation with an ophthalmologist is essential. Each person's situation is unique, and tailored counseling ensures the best results. As we've explored in this article, Tobrax offers a powerful solution to many bacterial eye infections, but knowledge, awareness, and proper treatment are key to realizing the full benefits of this treatment.

טיפות דמעות הן תמיסות רפואיות או קוסמטיות שמטרתן להקל על

ויטמין C הוא אחד הוויטמינים החיוניים ביותר לבריאות העיניים, הודות
מרכז מומחים לאבחון וטיפול מתקדם בתסמונת העין היבשה ומחלות פני שטח העין