טיפות דמעות – מה זה ולמה משתמשים בהן?
טיפות דמעות הן תמיסות רפואיות או קוסמטיות שמטרתן להקל על
Internal barley in the eye, also called horediolum, is an acute and localized inflammation that forms inside the sebaceous glands of the eyelid. The inflammation is caused by a bacterial infection, usually by the staphylococcus bacterium. Internal barley can cause pain, swelling and redness in the affected eye. Here we will discuss the causes of internal barley, signs and symptoms, diagnosis, treatment and prevention of the condition, with special reference to innovative treatments and recent research in the field.
The main cause of internal styes in the eye is a bacterial infection. The most common bacteria that causes internal barley is Staphylococcus aureus. This bacteria is often found on the surface of the skin and on the scalp, and it can penetrate the sebaceous glands of the eyelid and cause an infection.
In addition, there are internal and external risk factors that increase the likelihood of developing internal barley. Internal factors include a weakened immune system, diabetes, and other chronic medical conditions. The external risk factors include poor hygiene of the eyelids, use of contact lenses without proper cleaning, and use of expired or contaminated perfumes.
It should be noted that internal barley in the eye can appear at any age, but there are situations in which it is more common, such as among children and people with chronic immune system problems. It is important to know the various causes of internal barley in the eye in order to prevent and deal with the situation in the best way.
Internal barley in the eye is characterized by several clear signs and symptoms that can be easily recognized. The main symptom is a painful and swollen lump that appears on the eyelid, and is often accompanied by redness and localized heat. The lump can cause discomfort and sometimes also itch.
On top of that, people with internal barley may experience sensitivity to light and increased tearing. In some cases, the infection can cause significant swelling that makes it difficult to open the affected eye. In addition, there are cases in which a bad smell appears from the infected eye, and there may even be a purulent discharge.
Internal barley differs from external barley in that it appears inside the eyelid and not at its edge. Therefore, the lump that appears in internal barley may be less visible from the outside, but more noticeable from the inside. Severe pain and swelling can indicate a more serious infection that requires medical attention.
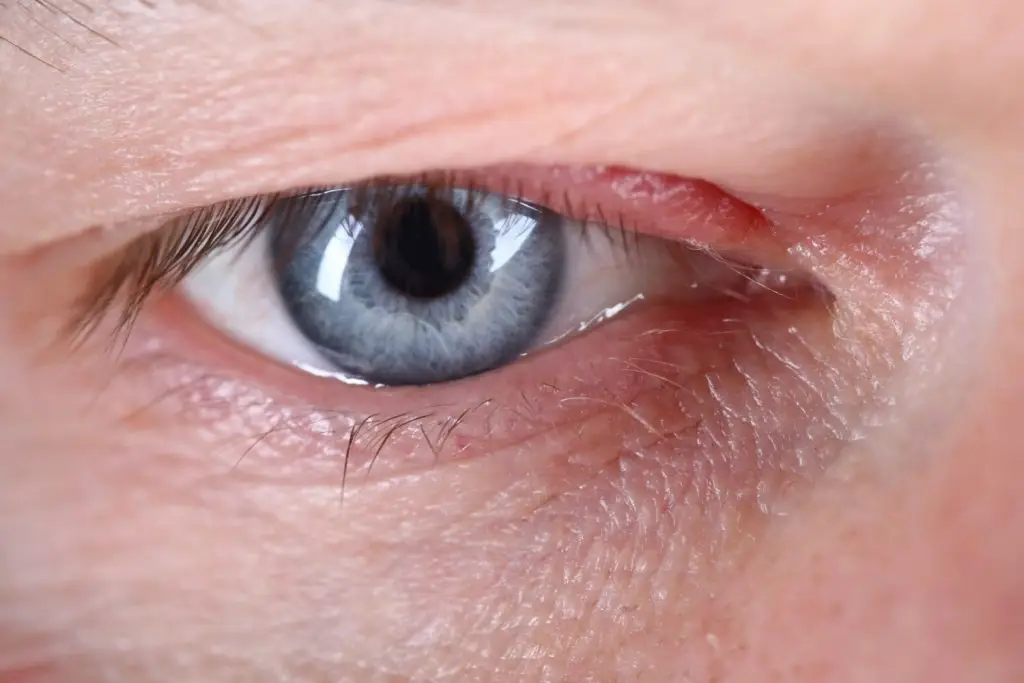
Diagnosing internal barley in the eye is usually performed by an ophthalmologist or family doctor. The diagnosis begins with a detailed medical anamnesis, in which the doctor will ask the patient about the symptoms, how long they have existed, and whether there have been similar events in the past.
The doctor will then perform a physical examination of the eye and eyelids. In this test, the doctor may use special devices such as a flashlight or a slit lamp in order to illuminate and examine the infected area more precisely. The examination will include examining the lump, assessing the swelling, redness and pain, as well as looking for signs of purulent discharge or advanced infection.
In rare cases, when a serious infection or complication is suspected, the doctor may perform additional laboratory tests, such as a culture from the eyelid, in order to identify the bacteria causing the infection and adjust an accurate antibiotic treatment. A differential diagnosis will also be examined to make sure that it is not a case of other conditions such as chalazion or an eyelid tumor, which can present similar symptoms.
The treatment of internal barley in the eye includes several options, depending on the severity of the condition and the patient's response to the initial treatments.
In the initial stages, home treatment may be effective. One of the simple and common ways is to place warm compresses on the infected eye for 10-15 minutes, several times a day. The heat helps relieve the pain and promote the drainage of pus from the lump.
In cases where home treatment is not sufficient, the doctor may recommend drug treatment. Usually, local antibiotic treatment will be given in the form of eye drops or ointment, which will help prevent the spread of the infection and promote recovery. In more severe cases, oral antibiotics may be needed.
If the conservative treatments fail to relieve the symptoms and the lump does not disappear, surgical intervention may be necessary. The process includes opening and draining the lump under local anesthesia. This is a simple and quick procedure, but must be performed in a clinic by a trained ophthalmologist.
In repeated or chronic cases, the doctor may examine the deep causes of the problem and offer additional preventive treatments, such as careful cleaning of the eyelids or the use of special treatments for chronic problems of the sebaceous glands in the eyelid.
Internal barley in the eye usually passes within a few weeks without significant complications, but in some cases malfunctions may appear that could worsen the situation.
One of the common complications is the spread of the infection to nearby tissues, which may cause eyelid inflammation (blepharitis) or an eyelid abscess. In rare cases, the infection can spread to the chimney area and cause inflammation of the chimney (orbital cellulitis), a serious condition that requires urgent treatment.
Another complication is calcification, a condition in which the lump does not clear and becomes a chronic, non-inflammatory nodule in the eyelid. The chalazion can cause chronic swelling and sometimes requires surgery to remove it.
Internal styes can also leave scars on the eyelid, especially if the infection is severe or if surgical treatment is performed to drain the lump. These scars may cause distortion of the eyelid or affect the aesthetic appearance of the eye.
Finally, if the stye is not treated properly, it may come back again and again, which may indicate a chronic problem with the sebaceous glands of the eyelid or a weakened immune system. In such cases, a comprehensive medical examination must be performed and the underlying causes of the problem treated in order to prevent the infection from recurring.
Prevention of internal barley in the eye focuses mainly on good hygiene and maintaining the health of the eyelids. Here are some important steps that can help prevent the development of internal barley:
First, it is important to clean your hands before touching your eyes. Bacteria on the hands can transfer to the eyelids and cause an infection. Using soap and water or hand sanitizer is an effective way to keep your hands clean.
Second, you should avoid rubbing your eyes, especially when your hands are not clean. Rubbing the eyes can introduce bacteria into the sebaceous glands of the eyelid and lead to the development of styes.
In addition, careful cleaning of the eyelids can help prevent the accumulation of oil and bacteria. You can use special wipes to clean the eyelids or suitable cleaning solutions.
Use of contact lenses should be in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions and maintain proper cleaning of the lenses. Avoid using damaged or old contact lenses.
In addition, make sure to clean the perfumes and make-up and avoid using expired products. Avoid sharing makeup products with other people, as this may transfer bacteria.
People with a tendency to recurrent internal warts can consider using regular cleaning wipes for the eyelids, and consult an ophthalmologist about additional preventive treatment options.
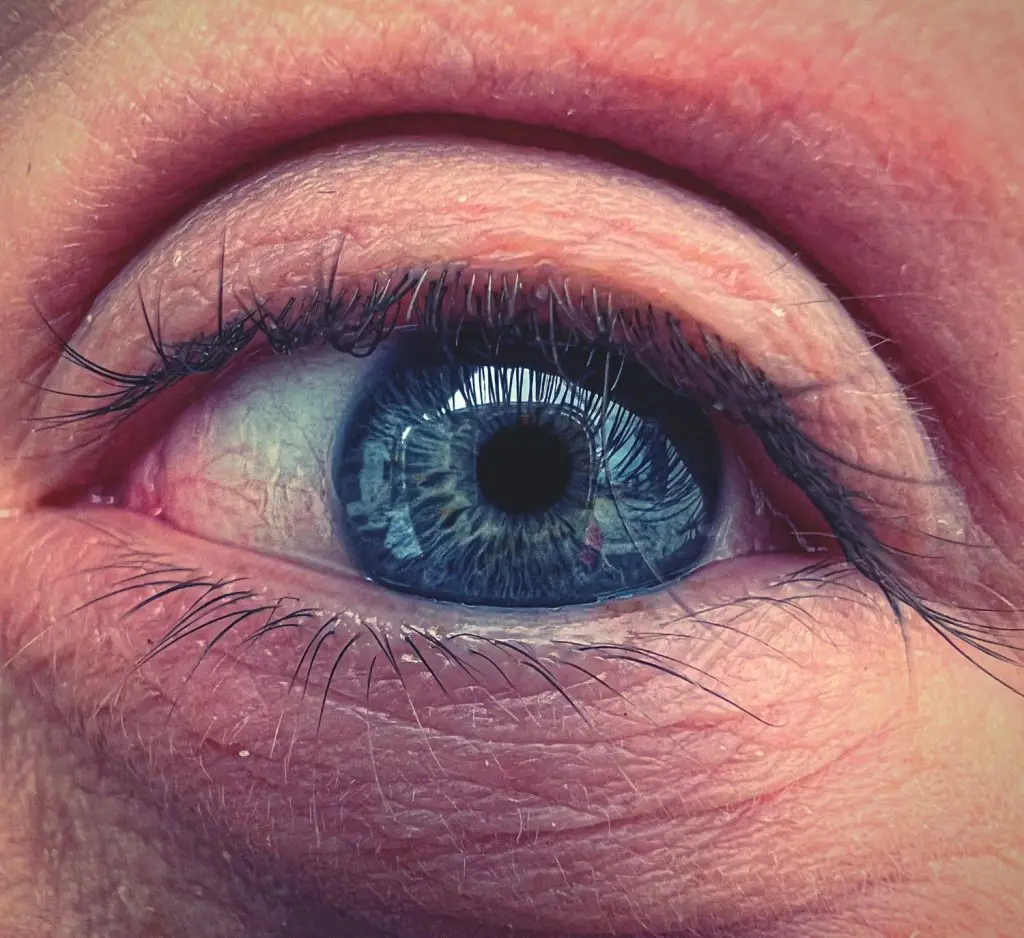
Internal barley in the eye can also appear in children, and it is especially common among children because of their tendency to rub and touch their eyes often. The barley can cause significant pain and discomfort in children, so it is important to know the ways of treatment and prevention in these cases.
In children, the symptoms of internal styes include swelling and redness of the eyelid, pain, sensitivity to light, and increased tearing. Children may also complain of a foreign body sensation in the eye or difficulty opening the affected eye.
Treatment of internal barley in children is similar to treatment in adults, but it is necessary to adapt to the child's age. Applying warm compresses to the affected eyelid can help relieve pain and promote drainage. It is important to explain to the child not to rub the eye and to keep the hands clean.
In more serious cases, when the compresses are not enough, a pediatrician or an ophthalmologist should be consulted. The doctor can recommend topical or oral antibiotic treatment, depending on the severity of the condition. Rarely, when the infection is severe or chronic, surgical treatment may be necessary to drain the lump.
Prevention of internal barley in children also focuses on good hygiene. Children should be taught to wash their hands regularly and avoid touching their eyes. In addition, it is necessary to keep the eyelids clean and avoid using products that can cause infection. By following these steps, you can reduce the risk of developing internal cataracts in the eye in children.
In recent years, there has been significant progress in the treatment of internal barley in the eye, with an emphasis on the development of innovative treatments and research aimed at better understanding the causes and the most effective treatments. One of the main innovations is the use of a laser to treat internal barley. Laser treatment can help drain the lump in a precise and targeted manner, with less pain and a faster recovery compared to traditional surgery.
In addition, there are new studies that focus on the use of advanced technologies for early and accurate diagnosis of internal barley. These studies include the development of innovative diagnostic tools such as thermal cameras and advanced ultrasound, which enable early and accurate identification of the barley and the state of contamination.
Another area of research is understanding the biological and genetic mechanisms that lead to the development of internal barley. These studies focus on identifying the genetic and environmental risk factors, and can lead to the development of personalized treatments based on the patient's genetic profile.
Also, there are new studies in the field of drug treatment, which test the effectiveness of new antibiotics and advanced anti-inflammatory drugs. The studies are focused on finding drugs that can alleviate the symptoms and prevent the recurrence of the barley more effectively.
In general, the research and innovations in the field are aimed at improving the ability to diagnose and treat internal barley more accurately and efficiently, with fewer complications and side effects. The continuation of the research in this field is expected to lead to further improvements in the treatment and prevention of internal barley in the eye.
Internal barley in the eye is a common phenomenon that can cause significant pain and discomfort. Through a thorough understanding of the causes and symptoms, internal barley can be treated effectively and reduce the risk of complications. Initial home treatment using warm compresses can sometimes be enough, but in more serious cases, appropriate medical treatment should be sought, including antibiotic or surgical treatment.
Prevention of internal barley includes maintaining hand and eyelid hygiene, avoiding rubbing the eyes and correct use of contact lenses. With children, it is important to adhere to the same principles and explain to them the importance of keeping the eyes clean.
The latest innovations and research in the field offer hope for further improvements in the treatment and diagnosis of internal barley, with an emphasis on new technologies and personalized treatments. The continuation of research and development in this field is expected to bring about significant improvements in the quality of life of patients with internal barley in the eye.
In the end, a thorough understanding of the condition, appropriate treatment and prevention can lead to a quick recovery and prevention of the recurrence of internal barley in the eye.

טיפות דמעות הן תמיסות רפואיות או קוסמטיות שמטרתן להקל על

ויטמין C הוא אחד הוויטמינים החיוניים ביותר לבריאות העיניים, הודות
מרכז מומחים לאבחון וטיפול מתקדם בתסמונת העין היבשה ומחלות פני שטח העין