
What is chronic blepharitis?
Chronic blepharitis is a common eyelid inflammation that affects the edges of the eyelids. Blepharitis usually involves both eyes and occurs when the oil glands near the base of the eyelashes become blocked, causing irritation and redness. The condition can be caused by a number of diseases and conditions such as certain skin diseases, infection or a combination. It is often a chronic disease that is difficult to treat, that worsens at times and can cause a decrease in vision, but usually there is no serious and irreversible damage to the vision, and it is not contagious.
The main symptoms of blepharitis are an itchy sensation in the eyelids, redness in the eyes, tearing, a kind of scaling and peeling at the base of the eyelashes, a burning or stinging sensation in the eyes, Dryness , hypersensitivity to light (photophobia) and a feeling of discomfort like a foreign body in the eye. Symptoms are often more significant in the morningC
למידע נוסף ותיאום ייעוץ עם מומחה עיניים התקשרו:
או השאירו פרטים ונשוב אליכם בהקדם
What types of blepharitis are there?
Anterior eyelid inflammation
Usually caused by bacteria (such as staphylococcus) or by dandruff from the scalp and eyebrows (seborrhoea). These bacteria are naturally found on the face and eyelids, but when their quantity is increased or when the body's reaction to them is intensified, inflammation or infection may appear. Less commonly, an allergic reaction or mite infestation of the eyelashes can cause anterior blepharitis.
Posterior blepharitis
Can occur when the sebaceous glands in the eyelids abnormally produce the fatty layer of the tears, whose function is to cover the area between the eyelid in front of the eye area, and delay the evaporation of the tears (thus keeping the eye moist). The resulting dryness is an environment that encourages the growth of bacteria. Posterior eyelid inflammation can also develop as a result of other skin diseases such as rosacea and scalp dandruff.
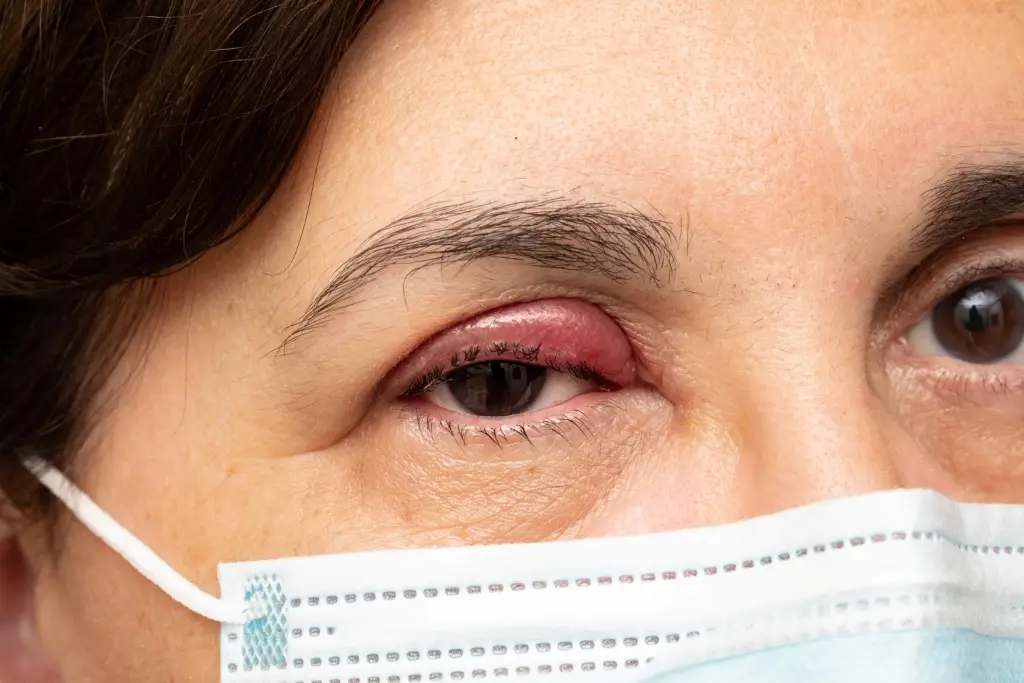
Who is at increased risk of developing blepharitis?
Those who suffer from the following conditions: dandruff in the scalp and face area, rosacea (a skin disease that causes redness and a kind of bumps on the face), oily skin and allergies that may affect the eyelashes.
Incidence of blepharitis:
Most types of blepharitis affect adults and children of both sexes. However, certain forms such as bacterial blepharitis (as a result of staphylococcus) occur mainly in women. Apparently the prevalence of the condition reaches up to half of the population so it is very common.

There are several possible causes for the development of blepharitis:
Bacteria that naturally exist on the eyelids that may in certain cases create an inflammatory reaction against them that manifests itself in blepharitis
Seborrheic dermatitis or rosacea
Dandruff on the scalp and face
Parasites such as demodex (eyelash mite)
Dysfunction of the meibomian glands - the sebaceous glands
How is blepharitis diagnosed?
First, the ophthalmologist will start with an anamnesis – a medical questionnaire, and collect information about the complaints, the patient's general eye and medical history, and especially about the risk factors for the development of the disease as described. From there he is expected to proceed to a physical examination. Blepharitis can be diagnosed by an eye examination with special emphasis on the eyelid area and the front surface of the eyeball. The examination will include an assessment of the structure of the eyelids, the texture of the skin and the appearance of the eyelashes, the bases of the eyelashes and the openings of the sebaceous glands (Meibomian glands) using the light of the slit lamp and magnification. In addition, you should check the quantity and quality of tears to see if there are any abnormalities.

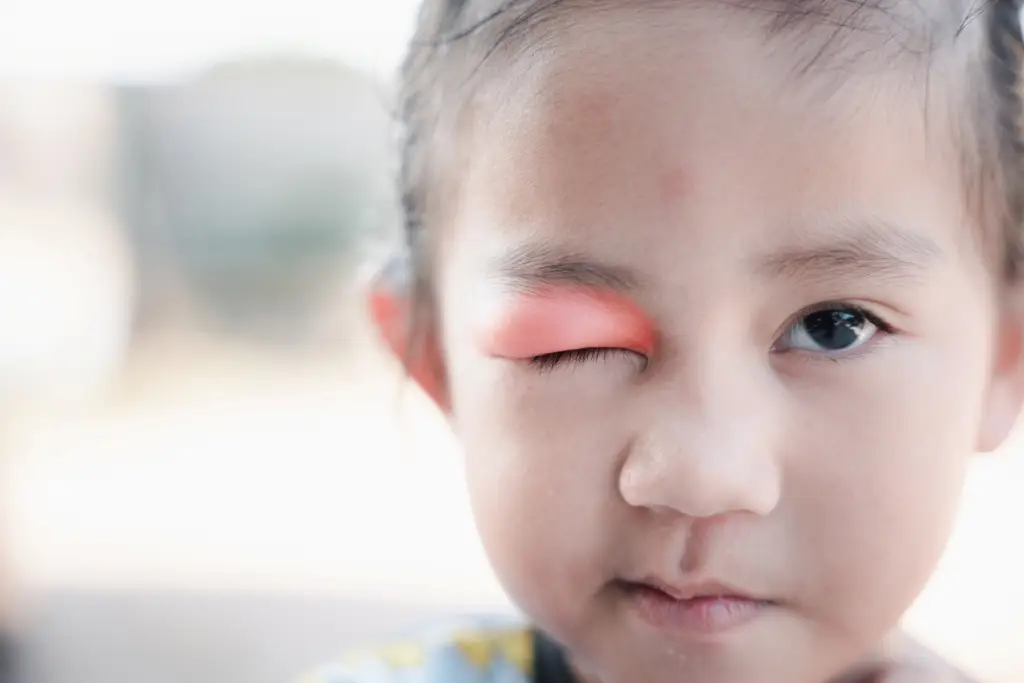
How can blepharitis be treated?
If signs and symptoms of blepharitis appear that do not seem to improve over time despite good hygiene – regular cleaning and treatment of the eyelashes, you should contact the doctor for assistance.
How can blepharitis be treated?
Unfortunately, there is no curative treatment for blepharitis, but some types of blepharitis can be treated independently at home in order to calm the symptoms and improve the condition. Some actions you can try:
1. Avoiding eye makeup
In order to reduce the irritation, at least until the blepharitis is on the mend and the infection is under control. In addition, you should avoid using joint makeup and be careful about its validity.
2. Applying warm compresses
You can use a clean cloth or towel and wet it with hot water (of course you should make sure the water is not too hot to avoid burns). Then squeeze the towel and gently place it on the eyelids. The operation must be repeated for a few minutes, and about 3-4 times a day. Eventually the fat in the glands will soften and it will be easier to remove them.
3. Cleaning the eyelids
Using a clean cloth with a mix of baby shampoo and water (50-50 ratio) or with dedicated wipes for cleaning the eyelids. The cleaning will be done in the morning and in the evening and will allow the removal of secretions, scales and pollutants.
If persisting in the treatment for a few weeks does not help, you should contact the attending ophthalmologist in order to receive more advanced treatment. The ophthalmologist may recommend:
Antibiotic treatment
Applying a prescription antibiotic ointment to the eyelid or using prescription antibiotic eye drops may help resolve the bacterial infection and reduce irritation. You should use the ointment before going to bed because it temporarily blurs your vision and can cause discomfort.
Anti-inflammatory treatment
Steroidal eye drops can be added to the treatment plan, although they are used mainly in severe cases. Steroids reduce the inflammatory reaction that the body creates, but it is important to remember that steroids may cause side effects such as an increase in intraocular pressure and cataracts, so it is important to use them in the correct dose, in a suitable indication and only under the instructions of the attending physician.
Treating the root of the problem
It is important to treat the causes that led to blepharitis in the first place, thus reducing the chance of the condition recurring. Skin diseases such as dandruff or rosacea, for example, can cause repeated flare-ups of blepharitis and require regular treatment.
Eye drops
Preservative-free tear substitutes can help deal with the feeling of dryness in the eyes and thus improve the blurred vision that patients report and the discomfort. The drops are bought without a prescription and are used as needed.
When should you see a doctor?
If signs and symptoms of blepharitis appear that do not seem to improve over time despite good hygiene – regular cleaning and treatment of the eyelashes, you should contact the doctor for assistance.
Complications of blepharitis:
Eyelash problems
Blepharitis can cause eyelashes to fall out, grow abnormally or become discolored.
Skin and eyelid problems
Long-term and chronic blepharitis may lead to scarring of the eyelids and their edge may turn inward or outward, which worsens the condition of dryness and may lead to scratching of the cornea by the eyelashes.
Dry eyes and increased tearing
Our tears consist of 3 important layers: aqueous, fatty and mucin. The layer of fat is produced in the meibomian glands in the eyelids, it covers the eye and inhibits the evaporation of tears. In blepharitis there is damage to the activity of the glands, which leads to an abnormal composition of the glands and dry eyes are obtained. In an attempt to compensate for the dryness, the eye produces more tears, therefore one of the symptoms that characterize dry eyes is actually an increased tear.
stye
stye is an infection that develops near the base of the eyelashes, and manifests itself as swelling or a painful bump.
Chalazion
A chronic condition also known as trapped stye. A small swelling which is not red or painful unlike stye. When a blockage occurs in one of the sebaceous glands (Meibomian glands) at the edge of the eyelid, inflammation develops in it - and this is stye. Sometimes, after the inflammation passes, granuloma tissue remains in the gland. The granuloma does not respond to local treatment and may remain on the eyelid for months or even years, and its treatment is surgical removal
Corneal injury
Constant irritation from the eyelids (due to the lack of fatty shielding) or eyelashes may damage the cornea to the point of erosion. Also, dry eyes increase the risk of developing an eye infection, since tears also have an immune function.


