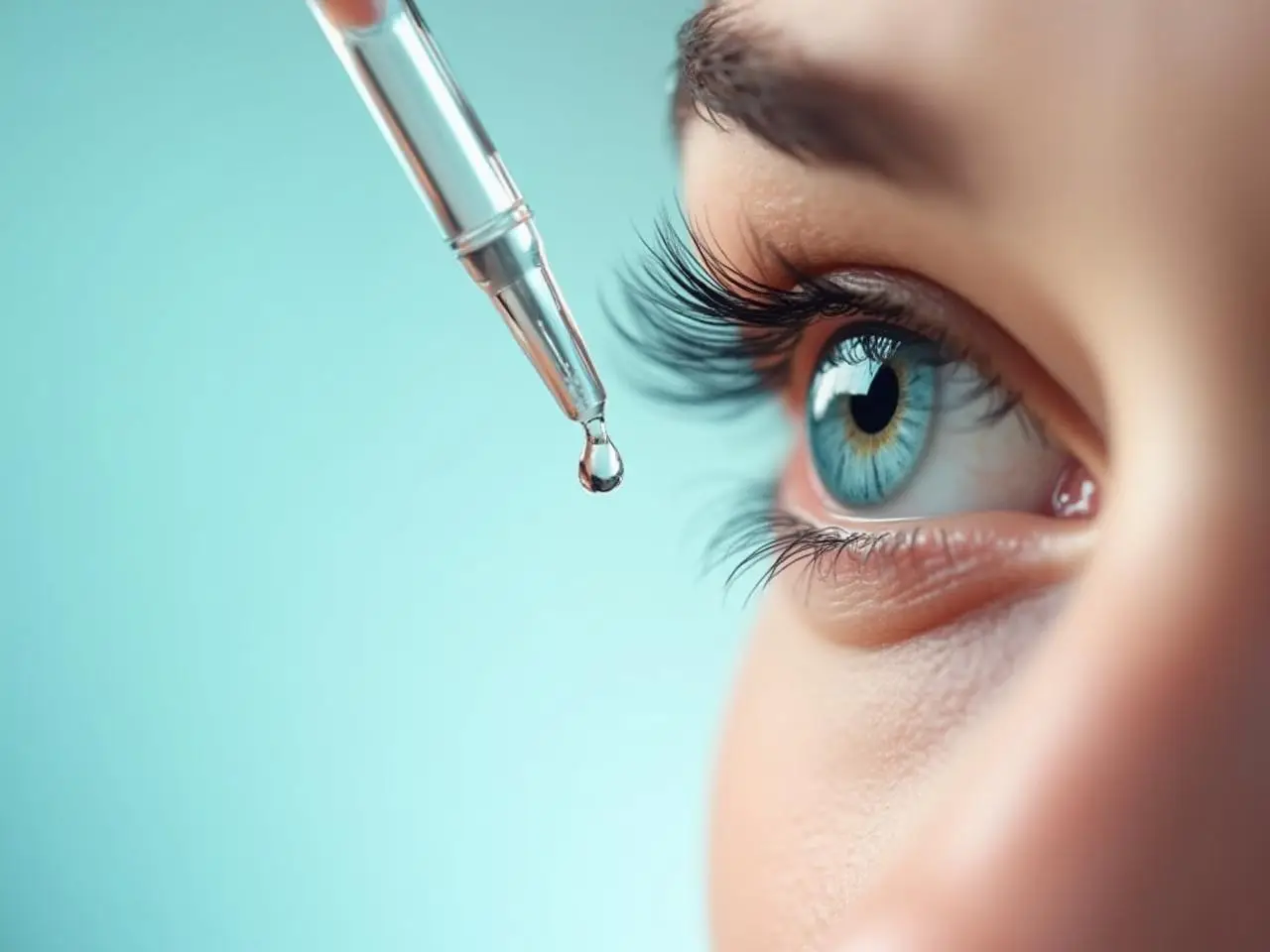
טיפות דמעות – מה זה ולמה משתמשים בהן?
טיפות דמעות הן תמיסות רפואיות או קוסמטיות שמטרתן להקל על
There are multiple possible causes of a cyst-like finding in the upper eyelid. The eye is a sensitive organ, and any discomfort or abnormality related to it, such as a cyst in the upper eyelid, can be worrisome. These cysts, although often benign, can cause patients cosmetic, functional or even symptomatic concerns. This article aims to shed light on the differential diagnosis, testing and treatment options for upper eyelid cysts.

Upper eyelid cysts can be confused with various other conditions. Accurate diagnosis is critical to effective management. Some differential diagnoses include:
1. stye in the eye – this is the most common cystic lesion of the eyelid, resulting from blocked meibomian glands. It presents as a firm and painless lump. Unlike hordeolum, it is not acutely inflammatory.
2. Horidiolum – this is an acute bacterial infection of the eyelid glands. External hordeolum affects the eyelash follicles and associated glands, while internal hordeolum involves the meibomian glands. These appear as painful erythematous swellings.
3. Dermoid cyst: These are congenital cysts that can appear on the eyebrow or upper eyelid. They grow slowly and can contain tissues such as hair, fat and even bone.
4. Mammary cyst: they originate from blocked mammary glands, these are filled with a cheesy and white substance.
5. Molluscum – a viral infection that can cause small dome-shaped papules with a central navel.
6. Basal cell carcinoma: Although it often appears as a painless nodule with a pearly appearance and possibly telangiectasia (tiny blood vessels), it can sometimes resemble a cyst.
7. Cysticercosis: a rare condition in which cysts form due to tapeworm parasitic infection.
To determine the exact nature of the cyst or differentiate it from other conditions, a series of clinical tests and evaluations may be necessary:
1. Clinical examination: The first step is a thorough examination, including history taking. Important details include its onset, duration, associated symptoms, any previous trauma or similar episodes in the past.
2. Slit lamp test: This provides a magnified view of the eyelid and can help differentiate between different conditions.
3. Ultrasound: A type B ultrasound examination is non-invasive and can help determine the contents of the cyst and its relationship to nearby structures.
4. Biopsy: In cases where malignancy is suspected, a biopsy is crucial. This involves taking a small tissue sample from the cyst for histopathological examination.
5. Blood tests: If cysticercosis or another systemic condition is suspected, blood tests may be required.
The treatment approach largely depends on the diagnosis:
1. Chalazion: the initial treatment includes warm compresses and lid massages. If the chalazion persists, it can be treated with intralesional corticosteroid injections or surgical excision.
2. Hordeolom: warm compresses are the main treatment. If a bacterial infection is suspected, topical or oral antibiotics may be prescribed. Persistent or recurrent cases may require incision and drainage.
3. Dermoid cyst: Surgical excision is usually the treatment of choice.
4. Mammary cyst: they can be surgically removed. If infected, antibiotics may be required.
5. Moloxacum – they can be treated with cryotherapy, therapy or local drugs.
6. Basal cell carcinoma: Excisional surgery, Mohs micrographic analysis, or other methods such as radiation may be used based on the size, location, and subtype of the tumor.
7. Cysticercus: This requires a combination of oral medications to kill the parasite and sometimes surgery to remove the cyst.
In addition to the specific treatments for each diagnosis, it is essential to treat any condition or contributing factors. For example, patients with recurrent hordeolum or chalazion may benefit from treatment of blepharitis or maintaining better eyelid hygiene.
An upper eyelid cyst, although often benign, can cause significant discomfort and concern to the patient. Correct diagnosis, treatment and care are essential to ensure the best results. It is essential to see an eye doctor if you notice any abnormalities in your eyelid or around the eye area. Early diagnosis and management can prevent possible complications and ensure the health of your eyes.

טיפות דמעות הן תמיסות רפואיות או קוסמטיות שמטרתן להקל על
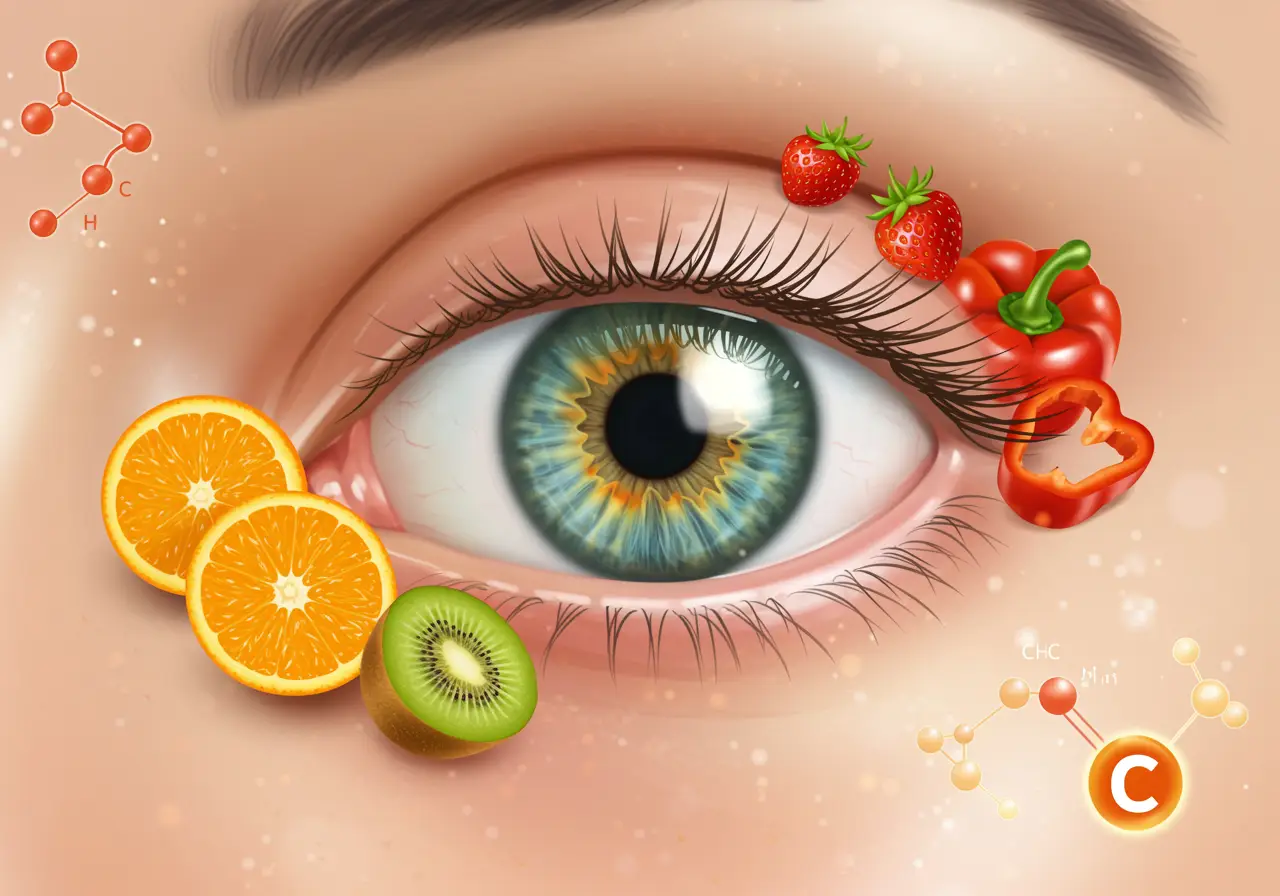

ויטמין C הוא אחד הוויטמינים החיוניים ביותר לבריאות העיניים, הודות
מרכז מומחים לאבחון וטיפול מתקדם בתסמונת העין היבשה ומחלות פני שטח העין