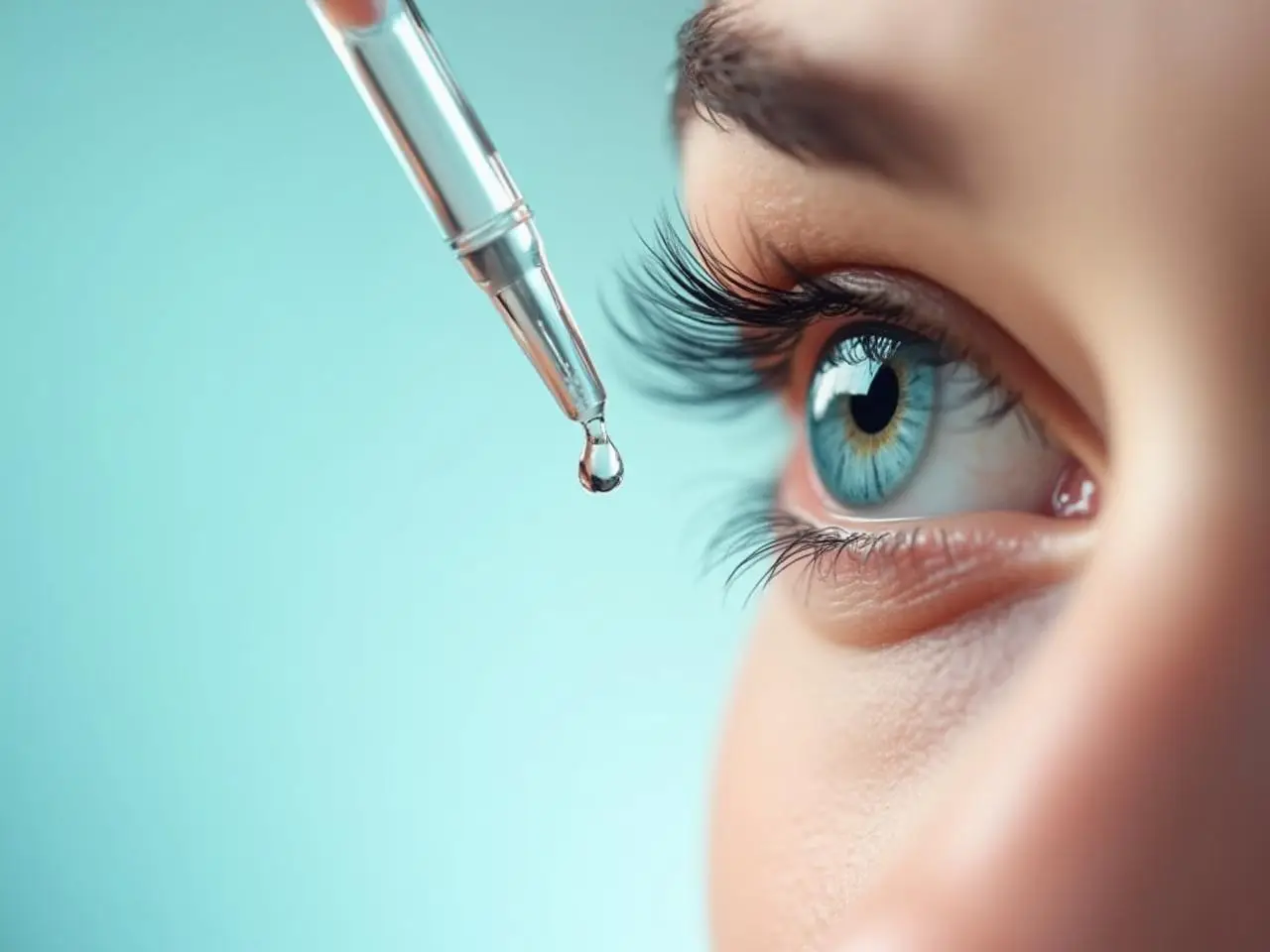
טיפות דמעות – מה זה ולמה משתמשים בהן?
טיפות דמעות הן תמיסות רפואיות או קוסמטיות שמטרתן להקל על
Blurred vision is a common problem that affects millions of people around the world. It can be a minor nuisance or a symptom of a serious health condition. This condition, characterized by a lack of sharpness and clarity in vision, can significantly affect the quality of life. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of blurred vision, delving into its various causes, the mechanics of human vision, diagnostic methods, treatment options and dealing with blurred vision in everyday life.

Understanding human vision requires looking into the complex structures and processes that allow us to perceive the world around us. Vision begins when light enters the eye through the cornea, the clear front surface of the eye. The cornea bends the light, which then passes through the pupil, the opening in the center of the iris, the colored part of the eye. The size of the pupil adjusts in response to the amount of light available, and controls the amount of light entering the eye.
After passing through the pupil, light reaches the lens, a flexible structure that changes shape to focus light rays on the retina, the light-sensitive layer of tissue at the back of the eye. The retina contains receptor cells, called cons & rods, that convert light into electrical signals. rods are responsible for seeing in low light levels, while cons are responsible for seeing color and fine details.
These electrical signals are transmitted to the brain through the optic nerve. The brain processes these signals, and converts them into images that we see. This complex process involves many factors, including the clarity of the visual aids, the health of the retina, the integrity of the optic nerve and the proper functioning of the visual centers in the brain.
Factors affecting visual acuity can range from refractive errors, where the shape of the eye does not bend light correctly, to conditions affecting the retina or optic nerve. Understanding the visual pathway is essential to understanding how various conditions and diseases can lead to blurred vision and how such conditions can be effectively treated.
Blurred vision can be caused by a myriad of causes, from temporary and benign conditions to more serious health conditions. Understanding these causes is the first step in finding appropriate treatment.
Refraction errors
Refractive errors are the most common cause of blurred vision. They occur when the shape of the eye prevents light from focusing properly on the retina. The main types of refractive errors include:
age-related reasons
As we age, our eyes undergo natural changes that can affect vision:
Environmental factors and lifestyle
External factors can also contribute to temporary blurred vision:
medical conditions
Several health conditions can lead to blurred vision as a symptom:
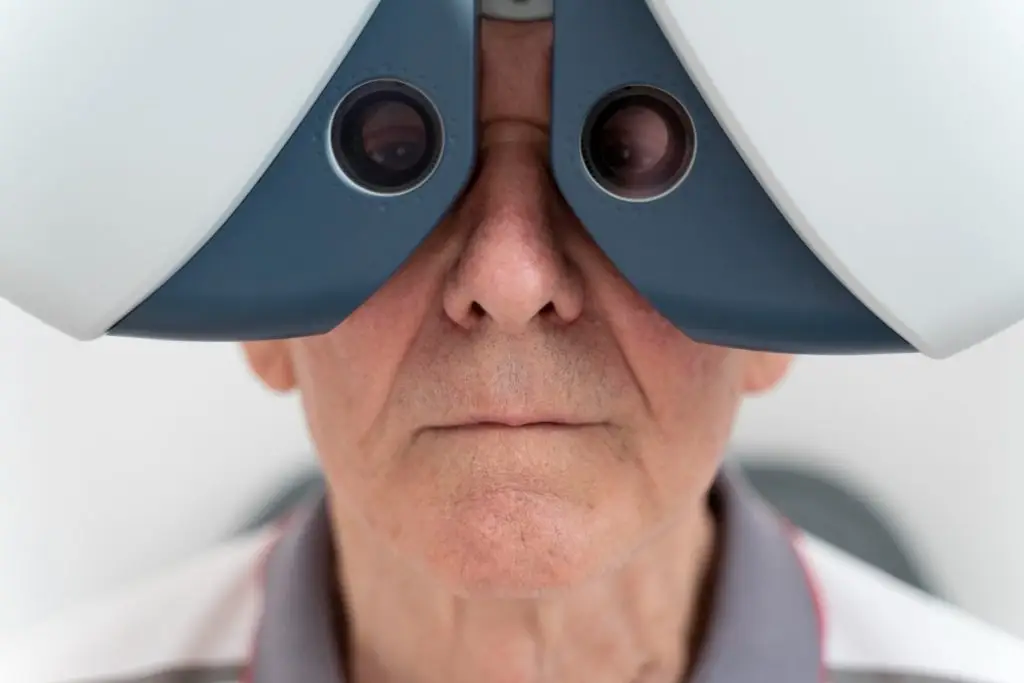
When experiencing blurred vision, it is essential to accurately diagnose the underlying cause in order to receive appropriate treatment. The diagnostic process usually includes the following steps:
when to seek help
Recognizing the signs that require medical attention is essential. An ophthalmologist should be consulted if they experience:
Comprehensive eye examination
A thorough eye exam is the cornerstone for diagnosing blurred vision. An optometrist or ophthalmologist will perform various tests:
Advanced diagnostic tools and techniques
Depending on the initial findings, additional tests may be used to investigate the causes of blurred vision:
Diagnosing the cause of blurred vision often requires a combination of taking a thorough medical history, physical examination and special tests. Accurate diagnosis is essential for effective treatment and management of the underlying condition.
Treatment of blurred vision depends on an accurate diagnosis of the underlying cause. Treatment strategies may vary from simple measures to more complex medical interventions.
Vision corrections
For refractive errors such as myopia, farsightedness and astigmatism, the main treatment includes corrective lenses:
Treatment of basic health conditions
When blurred vision is a symptom of an underlying health problem, treating the problem is a priority:
treatment and rehabilitation
In cases where the blurred vision cannot be fully corrected, vision rehabilitation can be recommended:
Living with blurred vision can be overwhelming with daily challenges, but various strategies and resources can help people cope and maintain their quality of life.
Lifestyle adjustments and home remedies
Simple changes can sometimes make a significant difference in managing the effects of blurred vision:
Blurred vision in everyday life
Adapting to blurred vision involves adjusting daily activities and environments:
Support systems and resources
A strong support system and knowledge of helpful resources can make a significant difference:
Living with blurred vision involves not only medical care but also making adjustments in daily life and seeking support. With the right strategies and resources, people can maintain their independence and continue to lead fulfilling lives.
Preventing blurred vision and maintaining optimal eye health involves a proactive approach and incorporating healthy practices into your daily life.
Protective measures and eye safety
Protecting your eyes from damage is fundamental:
Nutrition and lifestyle considerations
A healthy lifestyle can contribute significantly to eye health:
Periodic eye exams
Routine eye exams can catch problems early, often before any symptoms:

The field of vision care is developing rapidly, with groundbreaking research and technological progress paving the way for innovative treatments and solutions.
Technological progress in eye care
Emerging technologies are changing the diagnosis, treatment and management of eye diseases:
Research frontiers: stem cells, gene therapy and beyond
Innovative research provides promise for the future of vision care:
The role of public health in preserving vision
Public health initiatives play a crucial role in eye care, focusing on prevention, education and access to care:
Blurry vision can significantly affect a person's life, but understanding its causes, seeking appropriate diagnosis and treatment, and adopting preventive measures can greatly improve a person's quality of life. The field of vision care is advancing rapidly, offering hope and new solutions to those affected by vision problems. By maintaining eye health and adopting a proactive approach to eye care, people can protect their vision and maintain their independence and well-being for years to come.

טיפות דמעות הן תמיסות רפואיות או קוסמטיות שמטרתן להקל על

ויטמין C הוא אחד הוויטמינים החיוניים ביותר לבריאות העיניים, הודות
מרכז מומחים לאבחון וטיפול מתקדם בתסמונת העין היבשה ומחלות פני שטח העין