טיפות דמעות – מה זה ולמה משתמשים בהן?
טיפות דמעות הן תמיסות רפואיות או קוסמטיות שמטרתן להקל על
Barley is an infectious inflammation of the mammary glands in the eyelids, which manifests itself as a small, reddish lump that forms at the edge of the eyelid or inside the eyelid itself. The inflammation is usually caused by bacteria, especially staphylococcus bacteria, which naturally live on the human skin. When these bacteria enter the mammary glands, they can cause infection and the formation of barley. The stye can appear in one or both eyes, and it may be painful and itchy. Most of the time, the barley disappears on its own within a week or two, but in some cases it may require treatment of the barley with medical means.
External barley: This type of barley appears on the outer edge of the eyelid, usually at the base of the eyelashes. External barley is formed when there is an infection in the sebaceous glands located at the base of the eyelashes. The external barley is characterized by swelling, redness and pain in the inflamed area. You can sometimes see a point of pus at the end of the barley.
Internal styes: This type of styes appears inside the eyelid itself, and is caused by an infection of the oil-secreting glands inside the eyelid. Internal styes may be more painful than external styes and may sometimes cause more severe swelling of the entire eyelid. Internal barley is less common but can last longer and be more difficult to treat.
Understanding the differences between the types of barley can help choose the appropriate treatment and reduce pain and swelling more quickly.
The main symptoms of barley include swelling and redness of the eyelid, local pain and itching. A yellowish pus spot often appears at the end of the barley. In addition, you can feel heaviness and a feeling of discomfort in the inflamed eye. In more severe cases, there may be a feeling of pressure in the eye, general fatigue and sometimes local heat in the eyelid.
The diagnosis of barley is carried out by an ophthalmologist through a clinical examination. The doctor will examine the eyelid and evaluate the signs and symptoms to determine whether it is an external or internal barley. Rarely, in cases where the barley returns or if a more serious infection is suspected, the doctor may refer to additional tests such as bacterial culture or imaging tests to make sure there are no further complications.
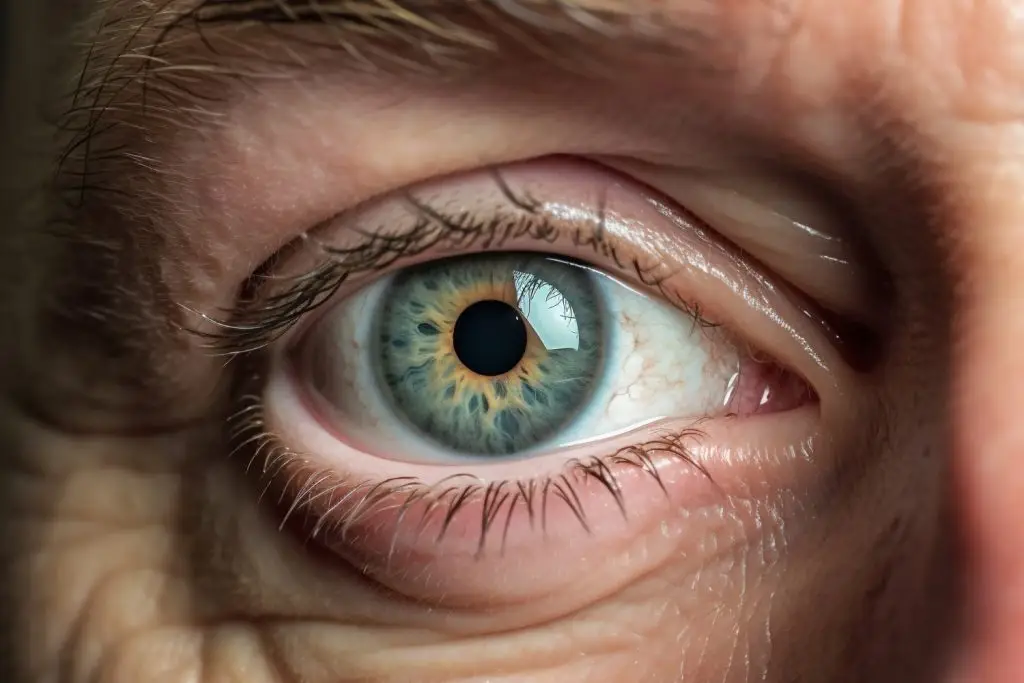
The initial treatment of barley is usually conservative, and includes the use of warm compresses. The hot compresses help to open the blocked glands and drain the accumulated pus, thus relieving the pain and swelling. Warm compresses should be placed on the inflamed eyelid for 10-15 minutes several times a day.
Maintaining eye hygiene is also important. Avoid rubbing your eyes and wash your hands well before touching your eyes. In cases of recurrent barley, it is recommended to make sure to clean the eyelids daily using special solutions or lukewarm water and mild soap.
The use of antibiotic drops and ointments may be required in cases where there is a fear of a significant bacterial infection. The drops and ointments contain antibiotics that help eliminate bacteria and reduce inflammation. The drops and ointments must be used according to the doctor's instructions and be sure to finish the full treatment.
Most of the time, these conservative treatments are enough to heal the barley within a few days to two weeks. If the barley does not disappear or if there is a worsening of the symptoms, you should consult a doctor for further examination and treatment.
In cases where conservative treatments are not sufficient, or when the barley is severe and accompanied by a more extensive infection, you can turn to drug treatments. One of the options is the use of local antibiotics in the form of eye drops or ointments. This antibiotic helps to eliminate the bacteria that cause the infection and reduce the inflammation. These drugs must be used in accordance with the doctor's instructions and for the full recommended period to prevent the infection from returning.
In cases of more severe inflammation, the doctor may recommend the use of anti-inflammatory drugs, such as topical steroids. These drugs help to reduce the inflammation and pain associated with barley, but they should be used with caution and in accordance with the doctor's instructions to avoid possible side effects.
In cases where the barley does not disappear after local treatment, or when there are signs of a more widespread infection, the doctor may recommend oral antibiotic treatment. This treatment is given when it is necessary to treat the infection in a systemic way and ensure complete elimination of the bacteria.
When conservative and medicinal treatments are not enough or when faster and more immediate treatment is needed, you can turn to invasive treatments. One of the common treatments is surgical drainage of the barley. In this process, the doctor makes a small incision in the barley to drain the accumulated pus and reduce the pressure and pain. It is a relatively simple procedure performed under local anesthesia and does not require hospitalization.
In addition, there is an option for laser treatments to treat barley. The laser makes it possible to get rid of the infection accurately and quickly, and reduces the risk of scarring or additional damage to the eyelid. The laser is used to heat the inflamed area and open the blocked glands, thus helping to drain the barley and reduce the inflammation.
It is important to emphasize that invasive treatments are performed only in cases where other treatments are ineffective or when there are complications that require immediate treatment. Before any invasive procedure, you should consult an ophthalmologist specialist and get all the necessary information about the risks and benefits of the treatment.
Besides the conservative and medicinal treatments, there are also home and natural treatments that can help alleviate the symptoms of the barley and speed up the recovery process. One of the popular home treatments is the use of warm compresses. Hot compresses can be made using a clean cloth dipped in hot water and placed on the inflamed eyelid for 10-15 minutes, several times a day. The hot compresses help to open the blocked glands and drain the accumulated pus.
Another treatment is maintaining the hygiene of the eyes and eyelids. Wash the eyes gently with lukewarm water and avoid rubbing or touching the dirty eyelids. It is also recommended to keep the pillows and towels that are used to clean the face and eyes clean to prevent the spread of bacteria.
Treatments with the help of plants are another option for natural treatment of barley. Warm compresses with chamomile or green tea extracts can help reduce inflammation and soothe the eyelid. In addition, aloe vera can be used to apply to the inflamed area, as it is known for its soothing and anti-inflammatory properties.
Using traditional remedies can also be effective in the treatment of barley. For example, you can use warm milk with a little turmeric to create a natural paste to apply to the barley. Turmeric contains natural anti-inflammatory substances that may help reduce inflammation and pain.
It is important to remember that although natural treatments can help, be careful and consult a doctor in case of worsening symptoms or lack of improvement after several days of home treatment.
Although barley is often a transient condition and not serious, there are possible complications that must be recognized and beware of. One of the common complications is cellulitis, which is an extensive inflammation of the soft tissues around the eye. This condition requires immediate medical attention, as it may cause significant damage to the eye and surrounding tissues.
Another complication is an eyelid abscess, which is formed when the barley does not heal and continues to accumulate pus. Such an abscess may require surgical drainage and antibiotic treatment to prevent the spread of infection.
In rare cases, the barley may lead to chronic inflammation of the eyelid (blepharitis) or the formation of an eyelid cyst. Chronic inflammation may cause eyelid dysfunction and recurrent infections, while a cyst may require surgical removal if it does not resolve on its own.
To avoid these complications, it is important to consult a doctor in case of worsening symptoms, severe swelling, high fever or signs of a wider infection. Early and correct treatment can prevent complications and ensure a quick and safe recovery.

Barley can be prevented by taking care of eye and face hygiene. First, avoid rubbing and touching your eyes with dirty hands. Wash your hands with soap and water before touching your face or eyes. Secondly, it is recommended to make sure to clean the eyelids daily with special solutions or lukewarm water and mild soap, especially for people who tend to develop barley often.
Using clean towels and pillows is an important part of maintaining eye hygiene. Towels and pillows should be changed regularly and laundered at high temperatures to kill bacteria. Avoid using old or shared cosmetics and make sure to replace them regularly.
People who use contact lenses should make sure to clean the lenses thoroughly and avoid using the lenses during an attack of barley or eye inflammation. It is also recommended to avoid excessive fatigue and stress, as these can weaken the immune system and increase the chance of barley formation.
Maintaining a balanced diet and drinking enough water are also an important part of preventing barley. A diet rich in vitamins and minerals, such as vitamin A and vitamin C, can help maintain eye health and the immune system.
You should consult a doctor in cases where the barley does not disappear after two weeks of home treatment or if there is a worsening of the symptoms. If the barley is accompanied by severe pain, severe swelling or high fever, you should see a doctor as soon as possible, as these may be signs of a more serious infection that requires medical attention.
When signs of a wider infection such as cellulitis or an abscess in the eyelid appear, a doctor should be consulted immediately. These signs include extensive swelling around the eye, severe redness, severe pain and difficulty opening the eye.
If there is repeated inflammation of the eyelids or if new symptoms appear that are not typical of barley, you should consult a doctor for a thorough examination and a correct diagnosis. In these cases, additional tests or more advanced treatments may be necessary.
Also, if the drug treatment given does not improve the condition or if side effects appear, the doctor should be consulted to consider alternative treatment options. Early and correct treatment can prevent complications and ensure a quick and safe recovery.
Barley is a common, inflammatory condition of the sebaceous glands in the eyelids, usually caused by bacteria. It manifests itself in swelling, redness and pain in the eyelid, and can sometimes be accompanied by a spot of pus. In most cases, barley disappears on its own within a week or two, but there are cases where medical treatment is necessary.
Conservative treatments such as warm compresses and maintaining eye hygiene can help alleviate the symptoms and speed up the recovery process. If necessary, there are drug treatments that include local or oral antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs. When conservative and medical treatments are not sufficient, invasive treatments such as surgical drainage or laser treatments can be considered.
Barley prevention is based on maintaining the hygiene of the eyes and face, avoiding rubbing the eyes and using clean towels and pillows. Also, it is important to make sure to clean the eyelids daily and maintain a balanced and healthy diet.
It is important to consult a doctor in cases of worsening symptoms, the appearance of a more extensive infection or lack of improvement after two weeks of home treatment. Early and correct treatment can prevent complications and ensure a quick and safe recovery.
In the end, dealing with barley requires a little patience and strict personal hygiene. By following the instructions and recommendations of the doctor, it is possible to prevent the recurrence of barley and maintain the health of the eyes.

טיפות דמעות הן תמיסות רפואיות או קוסמטיות שמטרתן להקל על

ויטמין C הוא אחד הוויטמינים החיוניים ביותר לבריאות העיניים, הודות
מרכז מומחים לאבחון וטיפול מתקדם בתסמונת העין היבשה ומחלות פני שטח העין